Difference between revisions of "RepRapBCN"
| (11 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Technical specifications== | ==Technical specifications== | ||
*Printing Volume: Length: 252mm, Width: 200mm, Height: 200mm | *Printing Volume: Length: 252mm, Width: 200mm, Height: 200mm | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Health & Safety== | ||
==LCD CONTROL== | ==LCD CONTROL== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 77: | ||
=='''CURA SOFTWARE: PREPARE STL'''== | =='''CURA SOFTWARE: PREPARE STL'''== | ||
| − | *Download Cura here: | + | *Download Cura here: https://ultimaker.com/en/products/cura-software |
==Machine settings== | ==Machine settings== | ||
| Line 82: | Line 84: | ||
[[:File:Custom RepRap information.png]] | [[:File:Custom RepRap information.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Object Settings== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:File:Object settings.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Print settings== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * | ||
| + | Basic settings are the general settings that you usually want to change. These settings have the most impact on the result | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nozzle size: The size of the hole in your nozzle. The FabLab uses 0.4mm nozzle by default, and 0.6 for faster printing or filaflex. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Layer height: The height of each layer. For print quality and printing time this is the most important setting. Usual settings are 0.2mm for a low quality print. 0.1mm for a medium quality print. 0.06mm for a high quality print. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Shell thickness: The thickness of the side shells, it has to be multiple of nozzle size number. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bottom/top thickness: The bottom/top thickness is the outer shell thickness on the top and bottom. it has to be multiple of layer height number | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fill density: Cura fills the internal parts of your model with a structure. This grid is made for strength and to support the top layers. The amount of infill you want is influenced by this setting. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Print speed: Print speed sets the speed at which the print is put down. The default of 50mm per second. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Print temperature: The print temperature is the temperature at which you print. if you want to print faster you might need to increase the temperature.210 for PLA and 240 for ABS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Support type: Supports are structures printed below the print to support parts that otherwise would be unprintable. There are 2 options here, support structures that need to touch the build platform, or support structures that can also touch the top of your model. You can modifie some aspects in(…) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Platform adhesion type: The platform adhesion type is a setting to help the printed object stick on the printer bed. Large flat objects might get lose from the printer bed because of an effect called warping. There is the option to use a raft, which is a thick grid under the object which scars the bottom of your print. Or a brim, which are lines around the bottom of your object and because of the larger area the corners are kept down. Brim usually gives the best results here as it does not scare the object. But it requires more room on the printer bed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Filament diameter: The filament diameter is the diameter of your filament. Reprap uses 2.9mm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Filament flow: The filament flow is a correction factor to make extrusion higher or lower than usual. Some systems or materials require a correction next to the usual diameter setting. This flow adjustment can be used for this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Maintenance== | ||
| + | ==Downloads== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:16, 22 January 2018
Contents
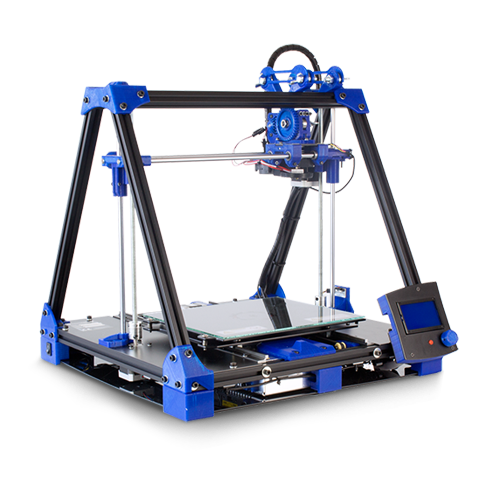
Technical specifications
- Printing Volume: Length: 252mm, Width: 200mm, Height: 200mm
Health & Safety
LCD CONTROL
- The BCN3D+ can be operated from its LCD menu, a single button combining two movements:
- 1- Turn to move through the menu.
- 2- Click to select desired option.
- Adjacently to the control button there is an emergency red button to stop the machine in case of malfunction. It stops the printer but keeps the screen and fans on. Once pressed, the printer resets itself to resume use.
SETTING UP YOUR BCN3D+
Hotbed height calibration
- For a proper use, the nozzle movement must be parallel to the Hotbed Surface.
To achieve that, there are three screws available to calibrate its orientation. There’s a risk of the nozzle hitting the hotbed glass or the first layer not sticking on its surface when decalibrated. The following steps must be followed:
- 1. Click Autohome (Prepare/Autohome) so the printer axes move to their initial position. The first time, caution should be exercised because the nozzle can collide with the base plate. If it is anticipated that this will happen, manually press the Z axis end stopper.
- 2. Adjust the screw triggering the endstop so the nozzle almost touches the glass when clicking Auto-home.
- 3. Tighten or loosen the three black screws levelling the base plate. The distance between the nozzle and the glass should be 0,2 mm. (Tip: use a folded paper to check)
- 4. Position the extruder in the left side using your hand (in case any resistance is felt, disable the stepper motors using Prepare > DisableSteppers). Level the base plate once again using the same procedure.
- 5. Move the base plate to the front to level the rear end of the plate.
- 6. Repeat the process until its four corners are levelled.
Load Filament
- 1. Heat the extruder. Warm the hotend up to printing temperature. It is not necessary to click on Preheat, although it is advisable when wanting to print immediately after loading the spool. If that is not the case, click Menú>Control>Temperatura>Nozzle>220ºC.
- 2. Click on Prepare>Move axis> 1mm>Extruder, and rotate the wheel slightly clockwise (positive values) to extrude a few millimeters of material. This procedure will help prevent jams.
- 3. Click on Prepare>Move axis> 1mm>Extruder, and rotate the wheel anticlockwise (negative values) moving the gear a few steps back until the filament is free.
- 4. Once the old thread is out, load the new one. Click on Prepare>Move axis> 1mm>Extruder so the screws hold it tight . Move the wire slowly until the material exits trough the end of the hotend.
- 5. For a proper filament feeding, the idler screws must be tightened enough, offering a slight resistance when assisted with our fingers.
- 6. Once the extruder starts pulling the filament, tighten the screws until enough pressure is reached.
- 7. Once these steps are followed, the filament will be loaded and ready to print.
FILAMENTS
PLA
PLA (polylactic acid) is the quintessential material for 3d printing, thanks to its ease of use through deposition. It is recommended to begin in this type of manufacturing technology with this material. A great variety of colors exists and complex geometries can be achived without great difficulty. The finish is slightly glossy or semi-matte. Printing is carried out at temperatures ranging between 195º and 220° C, depending on the supplier of the material and printing speed. A layer fan is required to build overhangs. It easily attaches to the glass, and if you work at a hotbed temperature ranging 45º C-55º C, no product is requiered to ensure this adherence. The mechanical properties are average, but presents a certain fragility in parts requiring deformation, from a temperature of about 50 °, the parts can present it. It is dissolved in caustic soda.
ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is one of the most widely used materials in 3d printing, and makes up for some of the weaknesses of the PLA. Printing with ABS is more complex and requires some attention. ABS is not recommended for inexperienced users. The variety of colors is also very high and the finish is semi-matte or matte. The ABS is printed at temperatures between 210º C and 240º C depending on the supplier of the material and printing speed. The ABS performs better with overhangs, and needs less air into the fan layer (excess air can be harmful). Adherence to the platform is weaker than with the PLA, due to material shrinkage on cooling, and often requires adhesive coating despite working with a hotbed temperature of 70 ° C. If the geometry of the piece to be printed has a too large base, is further promotes adherence problem due to the large lift effect that occurs at the oppopsite ends of the workpiece (known as warping).
Filaflex
Filaflex is a flexible material that comes in different colours. Requires the use of a 0.6 mm nozzle. Speed 10mm/s Temperature 235ºC Hodbed 40ºC
CURA SOFTWARE: PREPARE STL
- Download Cura here: https://ultimaker.com/en/products/cura-software
Machine settings
- STEPS: Toolbar/ Machine/ add new machine/ next/ other/ next/ custom/ next.
File:Custom RepRap information.png
Object Settings
Print settings
Basic settings are the general settings that you usually want to change. These settings have the most impact on the result
Nozzle size: The size of the hole in your nozzle. The FabLab uses 0.4mm nozzle by default, and 0.6 for faster printing or filaflex.
Layer height: The height of each layer. For print quality and printing time this is the most important setting. Usual settings are 0.2mm for a low quality print. 0.1mm for a medium quality print. 0.06mm for a high quality print.
Shell thickness: The thickness of the side shells, it has to be multiple of nozzle size number.
Bottom/top thickness: The bottom/top thickness is the outer shell thickness on the top and bottom. it has to be multiple of layer height number
Fill density: Cura fills the internal parts of your model with a structure. This grid is made for strength and to support the top layers. The amount of infill you want is influenced by this setting.
Print speed: Print speed sets the speed at which the print is put down. The default of 50mm per second.
Print temperature: The print temperature is the temperature at which you print. if you want to print faster you might need to increase the temperature.210 for PLA and 240 for ABS.
Support type: Supports are structures printed below the print to support parts that otherwise would be unprintable. There are 2 options here, support structures that need to touch the build platform, or support structures that can also touch the top of your model. You can modifie some aspects in(…)
Platform adhesion type: The platform adhesion type is a setting to help the printed object stick on the printer bed. Large flat objects might get lose from the printer bed because of an effect called warping. There is the option to use a raft, which is a thick grid under the object which scars the bottom of your print. Or a brim, which are lines around the bottom of your object and because of the larger area the corners are kept down. Brim usually gives the best results here as it does not scare the object. But it requires more room on the printer bed.
Filament diameter: The filament diameter is the diameter of your filament. Reprap uses 2.9mm.
Filament flow: The filament flow is a correction factor to make extrusion higher or lower than usual. Some systems or materials require a correction next to the usual diameter setting. This flow adjustment can be used for this.