Difference between revisions of "ShopBot"
| (32 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Shopbot_cutting.jpg ]] | + | [[File:Shopbot_cutting.jpg| thumb |ShopBot ATC PRS Alpha 3 Axes Milling machine - 4.27m x 2.31m x 1.70m]] |
| + | ==Technical Specifications== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cut / Movement Area: 3.71m x 1.57m x .2m | ||
| + | |||
| + | Machine dimensions(Footprint): 4.27m x 2.31m x 1.70m | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Health & Safety== | ||
| + | *Ensure you have been trained in the use of the CNC machine | ||
| + | *Inspect the equipment to ensure no obvious defects: damaged chuck, dull or cracked tools, damaged shields | ||
| + | * Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) | ||
| + | **Safety glasses | ||
| + | **Hearing protection | ||
| + | ** Non-slip shoes | ||
| + | * Remove rings, bracelets, watches, necklaces before work | ||
| + | *Tie back and confine long hair | ||
| + | * Wear tight-fitting clothing and/or roll up sleeves to prevent snagging | ||
| + | *Observe and check the cut progress until the end, don't leave the machine | ||
| + | *in case of emergency, pause the machine. Especially if the material begins to move, do not try to handle it with your hands. | ||
==CAM== | ==CAM== | ||
| − | *'''2D''' | + | *'''2D and 3D''' - RhinoCAM |
| − | + | ||
| + | After creating your milling strategy in RhinoCAM, it has to be transformed into a format that is readable by the shopbot's control system. | ||
| + | The piece of software performing this task is called a postprocessor. | ||
| + | Be sure to select the correct postprocessor '''"Shopbot MTC"''' as well as the expected file extension '''.sbp''' in RhinoCAM when exporting your milling program. | ||
==MCS== | ==MCS== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 33: | ||
*ShopBot 3 | *ShopBot 3 | ||
| − | == | + | ==Selecting the Right Bit for the Job== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''Milling Tools:''' A milling bit (also called milling cutter or end mill) is a tool used in CNC or hand-operated | |
| − | + | milling machines to remove material in a controlled manner to obtain a desired shape. This is usually done by | |
| − | + | moving the rotating tool sideways (laterally) through the material, thus cutting chips off the workpiece. | |
| − | + | Most milling bits can also cut in the direction of the tool axis, like a drilling bit. Vice-versa however, a drilling bit | |
| − | + | is designed to cut only axially to create cylindrical holes, and cannot be used for milling. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | '''Bit material:''' Router bits are made from a variety of materials. The most common are solid carbide, | ||
| + | carbide-tipped steel, and high-speed steel. Both solid carbide and carbide- tipped are good choices. | ||
| + | We do not recommend using high-speed steel bits as they dull quickly and must be re-sharpened. | ||
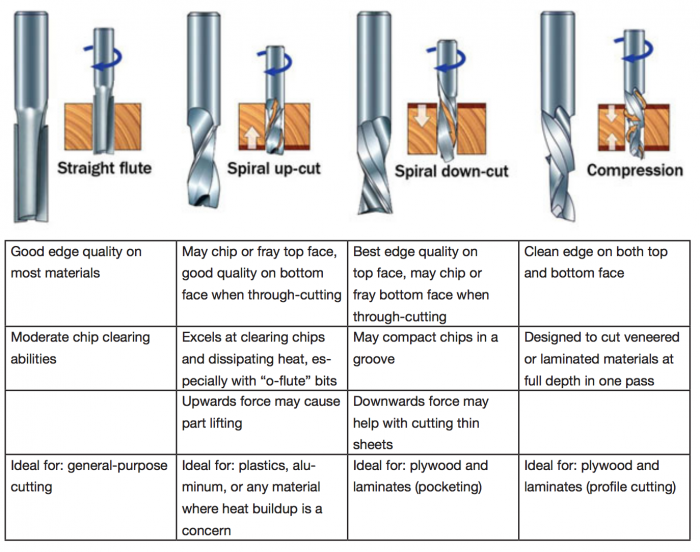
| − | '' | + | '''Flute type:''' There are four basic flute types: Straight, spiral up-cut, spiral down-cut, and compression. |
| + | Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are outlined in the chart below. | ||
| + | [[File:Schermata 2017-01-13 alle 17.01.41.png|700px]] | ||
==Parameters: Feeds and Speeds== | ==Parameters: Feeds and Speeds== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 56: | ||
should be fully understood before deviating from recommended settings. Bits choice is important in | should be fully understood before deviating from recommended settings. Bits choice is important in | ||
chip load, which is a representation of the size of the chips produced during cutting. The goal is to get | chip load, which is a representation of the size of the chips produced during cutting. The goal is to get | ||
| − | the maximum chip load possible to increase productivity, reduce heat, and prevent premature dulling. | + | the maximum chip load possible to increase productivity, reduce heat, and prevent premature dulling. |
When chip load is too small, bits will get too hot and dull quicker. When chip load is too high, the tool | When chip load is too small, bits will get too hot and dull quicker. When chip load is too high, the tool | ||
will deflect creating a bad surface finish and, in extreme cases, chip or break the bit. | will deflect creating a bad surface finish and, in extreme cases, chip or break the bit. | ||
| − | + | Optimising feed rates and speeds: | |
| + | |||
1. Start off using an RPM derived for the chip load for the material being cut (see charts). | 1. Start off using an RPM derived for the chip load for the material being cut (see charts). | ||
| + | |||
2. Increase the cutting speed (feed rate) until the quality of the part’s finish starts to decrease or the | 2. Increase the cutting speed (feed rate) until the quality of the part’s finish starts to decrease or the | ||
part is starting to move from hold downs. Then decrease speed by 10%. | part is starting to move from hold downs. Then decrease speed by 10%. | ||
| + | |||
3. Decrease RPM until finish deteriorates, then bring RPM back up until finish is acceptable. | 3. Decrease RPM until finish deteriorates, then bring RPM back up until finish is acceptable. | ||
| − | 4. This | + | |
| + | 4. This optimises RPM and speed to remove the largest possible chips. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Download the tool library for RhinoCam here:''' | ||
| + | [[File:Iaacp59 millingbits (1).zip]] | ||
| + | |||
'''Feeds and Speed:''' | '''Feeds and Speed:''' | ||
| − | |||
| + | *PLYWOOD | ||
Flat 6mm, 1 flute | Flat 6mm, 1 flute | ||
| Line 59: | Line 93: | ||
| − | FOAM | + | *FOAM |
Flat 6mm, 1 flute | Flat 6mm, 1 flute | ||
| Line 74: | Line 108: | ||
| − | CHIPBOARD | + | *CHIPBOARD |
Flat 6mm, 1 flute | Flat 6mm, 1 flute | ||
| Line 88: | Line 122: | ||
Step down: 4mm max (always depending on the diameter of the tool) | Step down: 4mm max (always depending on the diameter of the tool) | ||
| − | + | ==Use of SHOPBOT== | |
| − | + | '''Get ready''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
-Always wear safety glasses when operating the ShopBot or observing the machine when it is in use. | -Always wear safety glasses when operating the ShopBot or observing the machine when it is in use. | ||
| Line 103: | Line 135: | ||
-Securely fasten your material to the bed of the machine. Consult us every time you are faced with a different, challenging or unusual work-holding scenario. | -Securely fasten your material to the bed of the machine. Consult us every time you are faced with a different, challenging or unusual work-holding scenario. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Set the machine''' | ||
-Perform command “C3” Homing routine to establish the true machine home X-0 Y-0 (in the machine coordinates system) | -Perform command “C3” Homing routine to establish the true machine home X-0 Y-0 (in the machine coordinates system) | ||
| Line 108: | Line 142: | ||
-Jog X, Y to your personal Work Home coordinates, ie: the corner of your material & the X,Y origin of your drawing. | -Jog X, Y to your personal Work Home coordinates, ie: the corner of your material & the X,Y origin of your drawing. | ||
| − | -Take a photo of the Control PC screen or take note of the machine coordinates system to your chosen Work Home position. Example: X - 105.499, Y - 145.376 (do not worry about Z yet). Work Home X Y coordinates are simply offset measurements from the true Home (X-0, Y-0) of the Machine. | + | -Take a photo of the Control PC screen or take note of the machine [http://www.mesincuci.co/harga-mesin-cuci-toshiba-1-tabung-2017 Mesin Cuci Toshiba 1 Tabung] coordinates system to your chosen Work Home position. Example: X - 105.499, Y - 145.376 (do not worry about Z yet). Work Home X Y coordinates are simply offset measurements from the true Home (X-0, Y-0) of the Machine. |
-Zero work coordinates to X-0 Y-0 | -Zero work coordinates to X-0 Y-0 | ||
| Line 114: | Line 148: | ||
-Install tool in collet/tool holder + install tool/tool holder on spindle. | -Install tool in collet/tool holder + install tool/tool holder on spindle. | ||
| − | -Use command ”C2” & follow prompts on the PC screen (You will place the Z-0 plate directly under the tool on your material & place the Alligator Clip onto the collet nut on the tool holder) to set the Z-0 of your home position coordinates. You now have all 3 of your X, Y & Z work home coordinates loaded into the CNC system. | + | -Use command ”C2” & follow [http://www.mesincuci.co/harga-mesin-cuci-panasonic Mesin Cuci Panasonic] prompts on the PC screen (You will place the Z-0 plate directly under the tool on your material & place the Alligator Clip onto the collet nut on the tool holder) to set the Z-0 of your home position coordinates. You now have all 3 of your X, Y & Z work home coordinates loaded into the CNC system. |
| + | |||
| + | '''Send the file''' | ||
-Load part file, to choose the file you need to launch, you will see your “G-Code” which you generated in RhinoCam on the screen. | -Load part file, to choose the file you need to launch, you will see your “G-Code” which you generated in RhinoCam on the screen. | ||
| Line 128: | Line 164: | ||
-If you need to pause the machine, press the Spacebar on the PC Keyboard. The machine will pause, then follow the prompts to restart or end the process. | -If you need to pause the machine, press the Spacebar on the PC Keyboard. The machine will pause, then follow the prompts to restart or end the process. | ||
| − | -Emergency stop buttons are located in 2 places: On your remote, next to the Control PC, and On the end of the Y - Axis gantry. The Emergency Stop buttons are large, round Red buttons which will completely shut-down the machine. | + | -Emergency stop (E-stop) buttons are located in 2 places: On your remote, next to the Control PC, and On the end of the Y - Axis gantry. The Emergency Stop buttons are large, round Red buttons which will completely shut-down the machine. |
-Remove the tool-holder & tool from the spindle and store it in the tool-holder rack. | -Remove the tool-holder & tool from the spindle and store it in the tool-holder rack. | ||
| Line 135: | Line 171: | ||
-Skeletons and scraps created during the process should be cut up & placed in the recycling cart. | -Skeletons and scraps created during the process should be cut up & placed in the recycling cart. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Important commands== | ==Important commands== | ||
| Line 178: | Line 189: | ||
*[http://shopbotwiki.com/ ShopBot wiki] | *[http://shopbotwiki.com/ ShopBot wiki] | ||
| + | *[https://makezine.com/2014/09/10/endmills/ Makezine Article on end mills] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Maintenance== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Downloads== | ||
| + | [[File:Iaacp59 millingbits (1).zip]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Machines]] | [[Category:Machines]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:20, 31 March 2020
Contents
Technical Specifications
Cut / Movement Area: 3.71m x 1.57m x .2m
Machine dimensions(Footprint): 4.27m x 2.31m x 1.70m
Health & Safety
- Ensure you have been trained in the use of the CNC machine
- Inspect the equipment to ensure no obvious defects: damaged chuck, dull or cracked tools, damaged shields
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Safety glasses
- Hearing protection
- Non-slip shoes
- Remove rings, bracelets, watches, necklaces before work
- Tie back and confine long hair
- Wear tight-fitting clothing and/or roll up sleeves to prevent snagging
- Observe and check the cut progress until the end, don't leave the machine
- in case of emergency, pause the machine. Especially if the material begins to move, do not try to handle it with your hands.
CAM
- 2D and 3D - RhinoCAM
After creating your milling strategy in RhinoCAM, it has to be transformed into a format that is readable by the shopbot's control system. The piece of software performing this task is called a postprocessor. Be sure to select the correct postprocessor "Shopbot MTC" as well as the expected file extension .sbp in RhinoCAM when exporting your milling program.
MCS
- ShopBot 3
Selecting the Right Bit for the Job
Milling Tools: A milling bit (also called milling cutter or end mill) is a tool used in CNC or hand-operated milling machines to remove material in a controlled manner to obtain a desired shape. This is usually done by moving the rotating tool sideways (laterally) through the material, thus cutting chips off the workpiece. Most milling bits can also cut in the direction of the tool axis, like a drilling bit. Vice-versa however, a drilling bit is designed to cut only axially to create cylindrical holes, and cannot be used for milling.
Bit material: Router bits are made from a variety of materials. The most common are solid carbide, carbide-tipped steel, and high-speed steel. Both solid carbide and carbide- tipped are good choices. We do not recommend using high-speed steel bits as they dull quickly and must be re-sharpened.
Flute type: There are four basic flute types: Straight, spiral up-cut, spiral down-cut, and compression. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are outlined in the chart below.
Parameters: Feeds and Speeds
A challenge of getting a good CNC cut is in selecting the best bit, best cutting speed (feed rate) and router/spindle RPM (speed of rotation). Bits, feeds, and speeds are a critical part of machining and should be fully understood before deviating from recommended settings. Bits choice is important in chip load, which is a representation of the size of the chips produced during cutting. The goal is to get the maximum chip load possible to increase productivity, reduce heat, and prevent premature dulling. When chip load is too small, bits will get too hot and dull quicker. When chip load is too high, the tool will deflect creating a bad surface finish and, in extreme cases, chip or break the bit.
Optimising feed rates and speeds:
1. Start off using an RPM derived for the chip load for the material being cut (see charts).
2. Increase the cutting speed (feed rate) until the quality of the part’s finish starts to decrease or the part is starting to move from hold downs. Then decrease speed by 10%.
3. Decrease RPM until finish deteriorates, then bring RPM back up until finish is acceptable.
4. This optimises RPM and speed to remove the largest possible chips.
Download the tool library for RhinoCam here: File:Iaacp59 millingbits (1).zip
Feeds and Speed:
- PLYWOOD
Flat 6mm, 1 flute
RPM: 13000
Plunge: 1000
Travelling clearance plane: 4000
Rest of the parameters:2000
Step down: 4mm max (always depending on the diameter of the tool)
- FOAM
Flat 6mm, 1 flute
RPM: 12000
Plunge: 2000
Travelling clearance plane: 4000
Rest of the parameters:3500
Step down: 20mm max (always depending on the diameter of the tool)
- CHIPBOARD
Flat 6mm, 1 flute
RPM: 12500
Plunge: 1000
Travelling clearance plane: 4000
Rest of the parameters:2000
Step down: 4mm max (always depending on the diameter of the tool)
Use of SHOPBOT
Get ready
-Always wear safety glasses when operating the ShopBot or observing the machine when it is in use.
-Never leave the machine when it is in operation.
-If you need a bathroom break, the machine can be paused by pressing the Space Bar on the control PC keyboard.
-Make sure the bed of the machine is clean before use. Inform us if it is not clean.
-Securely fasten your material to the bed of the machine. Consult us every time you are faced with a different, challenging or unusual work-holding scenario.
Set the machine
-Perform command “C3” Homing routine to establish the true machine home X-0 Y-0 (in the machine coordinates system)
-Jog X, Y to your personal Work Home coordinates, ie: the corner of your material & the X,Y origin of your drawing.
-Take a photo of the Control PC screen or take note of the machine Mesin Cuci Toshiba 1 Tabung coordinates system to your chosen Work Home position. Example: X - 105.499, Y - 145.376 (do not worry about Z yet). Work Home X Y coordinates are simply offset measurements from the true Home (X-0, Y-0) of the Machine.
-Zero work coordinates to X-0 Y-0
-Install tool in collet/tool holder + install tool/tool holder on spindle.
-Use command ”C2” & follow Mesin Cuci Panasonic prompts on the PC screen (You will place the Z-0 plate directly under the tool on your material & place the Alligator Clip onto the collet nut on the tool holder) to set the Z-0 of your home position coordinates. You now have all 3 of your X, Y & Z work home coordinates loaded into the CNC system.
Send the file
-Load part file, to choose the file you need to launch, you will see your “G-Code” which you generated in RhinoCam on the screen.
-Visually check again the machine bed to ensure all tools have been removed and that material is securely fastened to the bed.
-Start in ShopBot software, follow prompts.
-Start the spindle with the green button on the ShopBot remote.
-Monitor the machine closely until the machine stops. Laser Cutters and CNC Routers have a high risk of fire if left unattended.
-If you need to pause the machine, press the Spacebar on the PC Keyboard. The machine will pause, then follow the prompts to restart or end the process.
-Emergency stop (E-stop) buttons are located in 2 places: On your remote, next to the Control PC, and On the end of the Y - Axis gantry. The Emergency Stop buttons are large, round Red buttons which will completely shut-down the machine.
-Remove the tool-holder & tool from the spindle and store it in the tool-holder rack.
-Clean the machine and your work area completely after you have removed your material.
-Skeletons and scraps created during the process should be cut up & placed in the recycling cart.
Important commands
Set Z zero
Run command C2. Put the metal plate under the machine head and connect the alligator grip to the tool head. Run Enter. The machine will go down and adjust its Z zero. Done.
Set XY zero
Run command C3. The machine will move. Wait. Done.
Change a toolpath tool
Run command 72 (press CN and then 72). The machine will leave its tool on its tool holder and will go to look for the new tool. Once the new tool is load the machine will move to the Z tool distance area in the toolpath. Connect the aligator grip to the tool head. The machine will go down and save the tool length. Done.