











🚀 Design for tomorrow: Explore MDEF!
New stories 👀 Read all about them!
Join us at 📍 FAB25 Czechia July 4–11 Brno & Prague!
🚀 Design for tomorrow: Explore MDEF!
New stories 👀 Read all about them!
Join us at 📍 FAB25 Czechia July 4–11 Brno & Prague!
We are a research and education centre rethinking the way we live, work and play!
Education Programs

In house programs
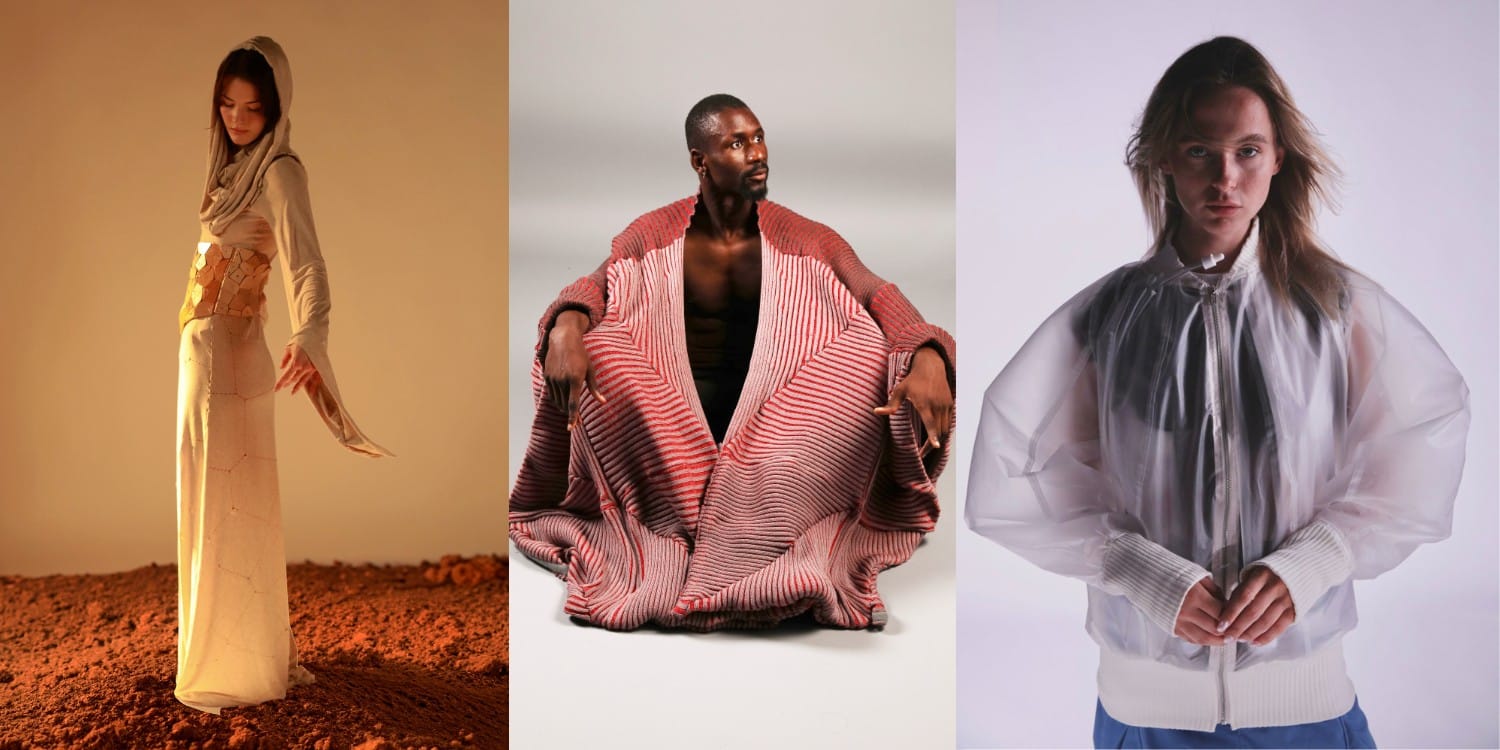
Master in Design for Emergent Futures – MDEF
Challenge the Way Things Work Today, Design for Tomorrow

In house programs
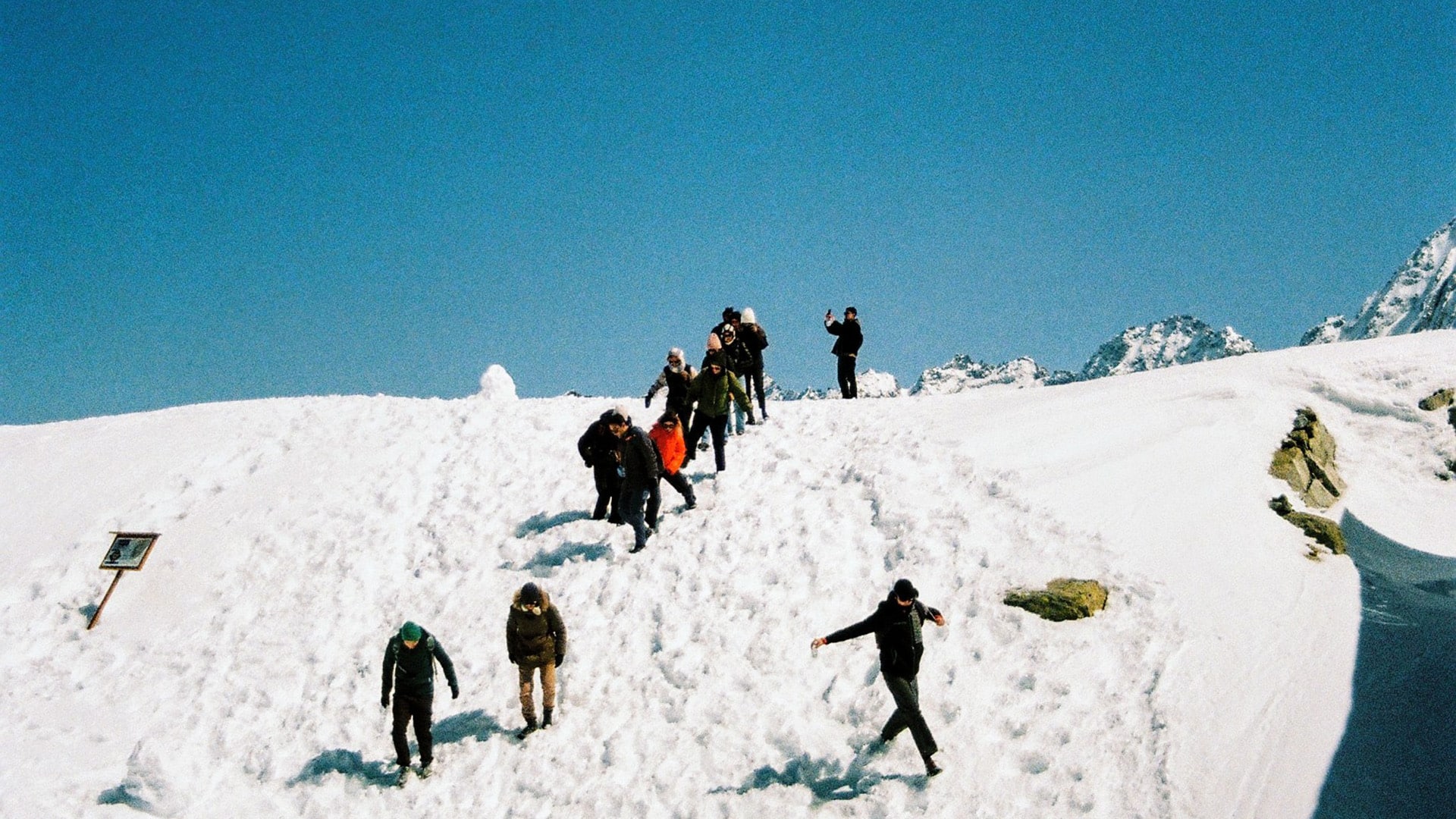
Postgraduate in Digital Fabrication – Fab Academy BCN
Hands-on learning experience and learn rapid-prototyping.
Our latest projects
Hot from the blog
Stay in the loop
RESOURCE
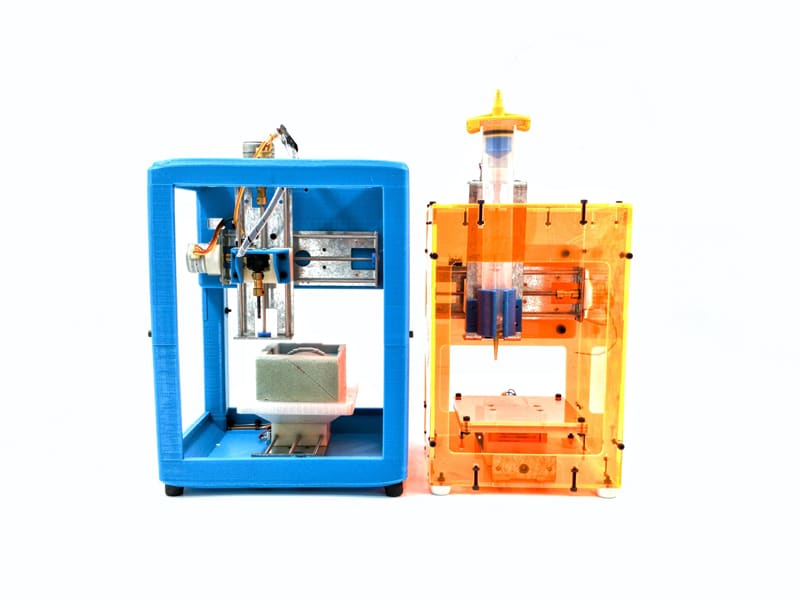
Fab City: The Mass Distribution of Almost Everything
A manual for making positive engaging urban futures possible
read more


RESOURCE
Fab City: The Mass Distribution of Almost Everything
A manual for making positive engaging urban futures possible
read more


RESOURCE
Fab City: The Mass Distribution of Almost Everything
A manual for making positive engaging urban futures possible
read more
🚀 Design for tomorrow: Explore MDEF!
New stories 👀 Read all about them!
Join us at 📍 FAB25 Czechia July 4–11 Brno & Prague!
🚀 Design for tomorrow: Explore MDEF!
New stories 👀 Read all about them!
Join us at 📍 FAB25 Czechia July 4–11 Brno & Prague!


















